Frequently Asked Questions about UPS’s.
What is a UPS?
A UPS is essentially an intelligent battery. It will ensure that whatever load it is supporting will be provided with a constant, clean source of power in the event of a power outage.
Why do I need a UPS?
Let’s say that your power is 99% guaranteed. This will still leave you without power for 8 hours each year. Not to mention the damage that bad power will do to equipment in general. As we become more and more reliant on outsourced power from European Countries, we are leaving ourselves wide open to prolonged power cuts, power that is of insufficient quality, and therefore our spend increases on equipment that is sensitive to bad power.
An additional word of warning:
“It is no longer possible to ignore the implications of the reliability and overall quality of our electrical supply. Without dramatic changes in the quality of electrical power coming into homes & businesses, everyone on the grid is vulnerable to significant damage and loss. Interruptions and disturbances in supply voltage can shut down, damage, and even destroy the equipment it is attempting to run. “
How does a UPS Work?
The UPS constantly checks to see if the incoming power is of sufficient quality to be used. If the power drops, or is cut off completely, the UPS transfers itself to battery, and will use the battery power until the main AC power is either of sufficient quality, or the power returns. If the power is not of sufficient quality, or there is insufficient battery life remaining, the software that comes with the UPS will shut down the PC it is supporting, ensuring that all data is saved correctly.
Are there different types of power problems?
Yes - there are many, but below are the main culprits to deal with:
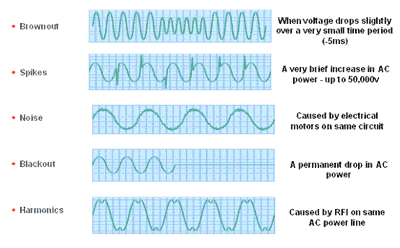
Are there different types of UPS?
Yes – there are primarily 3 types of UPS’s:
1. Offline
2. Line Interactive
3. Online
An offline UPS will take about 4-10 seconds to transfer to battery power, and hence is unsuitable for workstation/server environments. The line-interactive UPS will transfer between 4-6 milliseconds after a power cut, and an online UPS will have 0 transfer time between the power going out and the UPS kicking in.
What is the difference between single phase UPS’s and 3 phase UPS’s?
A single phase UPS will only supply single-phase power from a single-phase load. These UPS’s are normally only for smaller loads (up to 12Kva for example). A 3-phase UPS is a much larger unit, and can be fed with a 3-phase supply to produce either a single-phase output, or a 3-phase output.
How do I size a UPS?
If you multiply the Amperage of the load by the voltage, you can get a required VA rating. For example:
4 Amp load, 230 volts = 920va so a 1000va (or 1Kva) unit would be ideal.
What is “Runtime”?
Runtime is the length of time you need your UPS to run for. In some applications, a small runtime is require – 5 minutes or so. There are however, times when a much longer runtime is required. Some people need a UPS to run for 24 hours, for example.
Where can I use a UPS?
Practically anywhere there is a power requirement. UPS’s are not designed specifically for computers - there are thousands of applications a UPS can be placed into, and be expected to function perfectly. For example:
· Computer rooms – servers, PC’s, routers, hubs, alarms, etc.
· Communications – telecommunications, telephones, fax, modems, ADSL.
· Security – Alarm Systems, building management systems, et.
· Process Control – Manufacturing environments, PLC’s, etc.
· Medical & Health – Hospitals, emergency lighting, etc.
· Banking & Insurance - EPOS, ATM, etc.
· Home - Home pc’s, television, stereo, home entertainment systems, etc.
· Military - secure applications, etc.
What are the consequences of not using a UPS?
Let’s say you are in an area that provides bad quality power, or even regular power cuts. You own a shop that regularly gets cut off from mains supply. What happens?
1. Immediate loss of business
2. Backlog of work/loss of production
3. Deterioration of customer service
4. Loss of customer account management
5. Loss of financial Control
6. Loss of goodwill
7. Inability to pay staff
8. Financial Loss
9. Loss of operational data
10. Loss of customers
I would like to be able to get some more information on what you have outlines here - who can I speak to?
Please email [email protected] for additional information
Can I get training on UPS’s and ancillary products?
Yes, MGE can provide you with detailed training for groups between 3 - 300.
How long will a UPS last me?
A small UPS will normally last between 3-5 years, but if the UPS is constantly in operation, the lifetime will decrease incrementally. A larger UPS (3-phase) comes with either 5 year design life batteries, or 10 year design life batteries, so this span is indicative of how long it will last you.
Why should I buy a UPS?
- Over one third of companies take more than a day to recover from the disruption caused by a power failure. 10% take more than a week
- Because of a power failure, 33% of companies lose between £10 000 and £250 000, 20% lose between £250,000 and £1 million, 15% lose over £1 million
- Out of 450 leading companies surveyed, each suffered an average of 9 computer failures each year. (Source: Find FVP/Fortune 1000 companies)
- Following a power failure, it can take up to 48 hours to reconfigure a network system or a multi terminal environment.
- It can take days, weeks or even months to re-input lost data. Sometimes data is lost forever, for instance in CAD or graphics applications where original work can never be recreated
- Loss of market share, damage to a companies reputation, and loss of goodwill are not covered by insurance following a computer disaster
- Insurance claims take a long time to settle - well after the disaster has occurred
- 90% of all companies that experience a computer disaster and don't have a survival plan go out of business within 18 months (Source: Price Waterhouse)
- Power Failure is responsible for 28% of computer system breakdowns